What is a good posture?
A good posture is one in which a person’s body is optimally aligned in such a way that the muscles can perform actions, requiring least amount of energy to achieve the desired effect.
Good posture:
- Helps muscles work efficiently. Reduces the extra muscle tension required to either produce movement or maintain the posture. Is energy efficient.
- Helps to maintain a healthy back.
- Is a sign of healthy mental attitude and emotion. Reflects joy, confidence and happiness.
- Is aesthetically pleasant.
Poor posture can lead to:
- Cervical pain
- Shoulder pain
- Thoracic back pain (upper back pain)
- Lumbar back pain (lower back pain)
- Sacral region pain (hip pain)
- Pain radiating to limbs or pain in vital organs (due to pressure on nerve tissues of the spinal cord or the nerve roots)
- Pins and needles sensation and numbness in various body parts
- Muscle spasm
The nature of pain may vary from dull nagging pain, sharp piercing pain to hot throbbing pain, etc.
What does poor posture do to your body and how to rectify it?
The incorrect posture at work, recreation, exercise or in other daily routine activity puts constant strain on your body parts – especially back. This can lead to imbalance in smooth functioning of vertebral bodies, Inter-vertebral Discs, Ligaments, Muscles and Nerves, accelerating their degeneration and structural deformation.
Through vigilant maintenance of correct posture, the extra body strain can be reduced, thus bringing the related problems under control and also preventing their recurrence. The relaxation, mobility and strengthening exercises work wonders in maintaining a healthy static and dynamic posture.
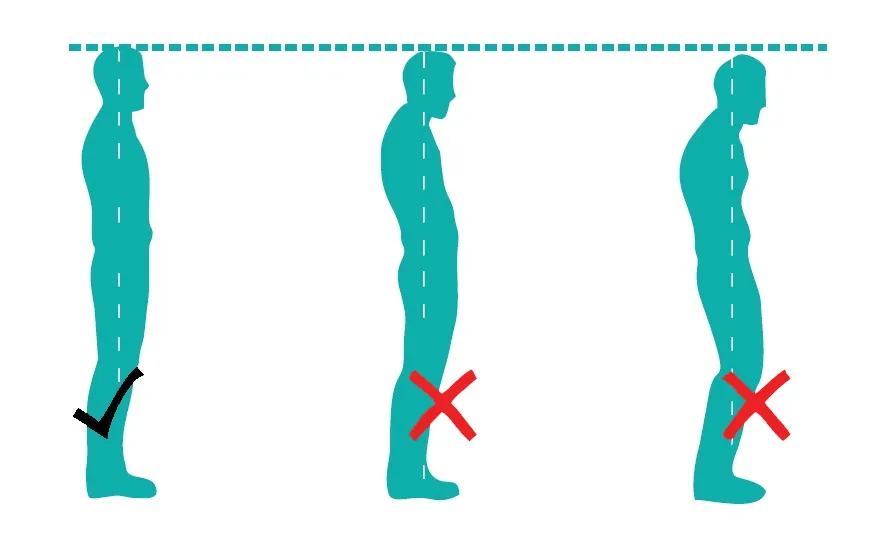
Standing Posture:
It is important to maintain the natural curve of the spine when standing. One should follow these guidelines while standing tall
- Stand with the feet hip width distance apart.
- Outer edges of the feet should be parallel.
- Keep your knees slightly flexed , thigh muscles contracted and buttocks contracted.
- The spine should be erect with shoulders relaxed.
- The chin should be parallel to the floor with neck tall for correct neck alignment.
For relaxed standing, follow the guidelines 3, 4, 5 with feet slightly apart, one foot in front of the other and knees slightly flexed. Use a box or slightly elevated area to prop one foot up while standing. Change feet position every 20 minutes.
Sitting Posture:
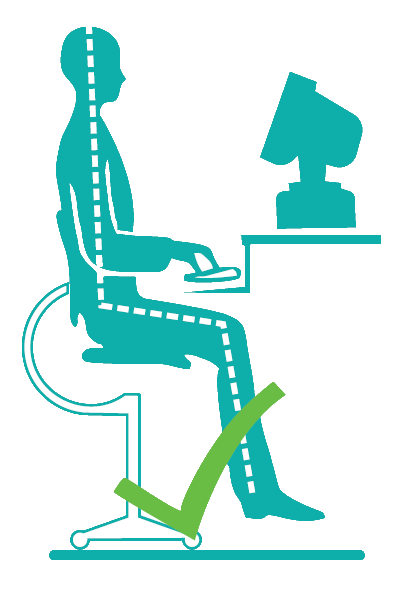
- Many problems which arise because of long sitting hours can be avoided by adopting correct sitting posture.
- Keep your neck tall while sitting.
- The top of your screen (if you are using a computer) should be at 10 degrees to your eye level.
- Shoulder should be relaxed while working (avoid hunchback and shrugging of the shoulders).
- Your forearms should be parallel to the floor while working.
- The chair should have a backrest that supports your back.
- The seat should completely support your thigh.
- There should be some gap between the edge of your seat and the behind of your knee.
- Your legs should be bent in 90- 110 degrees while sitting.
- Sit tall with feet flat on the floor or supported by a footrest.
- Take a break for stretches every 20 minutes.
- Use a coccyx cushion to give your spine the natural curve.
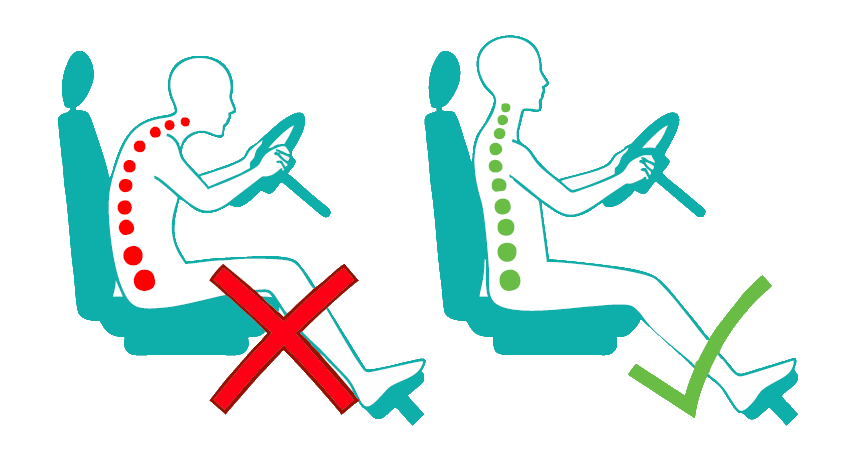
Driving Posture:
Always sit with your knees leveled with the hips. A rolled up towel or a back support cushion can be placed behind the back for proper support. Sit as close to the steering wheel as possible because reaching increases the pressure on the lumbar and cervical spine, shoulder and wrist.